Who Does It Affect
The term abnormal uterine bleeding primarily describes bleeding in non-pregnant people in their reproductive years. But this doesnt mean that irregular bleeding wont affect you if youre post-menopausal or pregnant.
If youre bleeding and have experienced menopause, contact your provider. Bleeding after menopause is never normal. Blood may be red, pink, brown or even rust-like in appearance.
You should also contact your provider if youre bleeding during pregnancy. Some causes are harmless, but others require medical attention, especially if the bleeding happens late in your pregnancy.
How Is Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Treated
Your treatment depends on whats causing your bleeding. Medications and surgical options are available to manage your bleeding or treat whats causing it.
Medications
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs , such as ibuprofen .
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists can temporarily stop or reduce bleeding by preventing ovulation.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists can manage heavy period bleeding related to fibroids.
Surgery
There are several procedures available to treat abnormal uterine bleeding. Ask your provider about how often they perform a given procedure. Seeing a provider who frequently performs a procedure often leads to faster recovery with fewer complications.
- Hysteroscopy. A procedure where your provider removes atypical structures in your uterus, like fibroids and polyps.
- Uterine artery embolization. Stops blood flow to fibroids, causing them to shrink.
- Myomectomy. Removes fibroids while keeping your uterus intact and preserving your ability to get pregnant and have children.
- Endometrial ablation. Destroys your uterus lining through the use of a laser, heat, electricity, microwave energy or freezing. You shouldn’t have this procedure if you want to get pregnant and have children.
- Hysterectomy. Removes your uterus. Hysterectomy is often used to treat cancer or cancerous changes in your endometrium. Advanced stages of cancer may need radiation or chemotherapy.
What Does Bleeding In Between Your Periods Mean
What does bleeding in between your periods mean?
What does it mean when a woman is bleeding but not on her period? Irregular vaginal bleeding is any bleeding from a womans vaginal area and usually refers to bleeding that is not part of a regular period. The range of causes includes infection and hormonal changes.
Does bleeding in between periods mean you are pregnant? Share on Pinterest Spotting may be an early sign of pregnancy. Light bleeding or spotting can be an early sign of pregnancy. This spotting is called implantation bleeding because doctors think that it happens when a fertilized egg attaches itself to the lining of the uterus.
Is it normal to have periods twice in a month? The average menstrual cycle is 28 days long but can vary from 24 to 38 days. If a menstrual cycle is shorter, a person can have a period more than once a month. While occasional changes in the menstrual cycle are not unusual, frequently experiencing two periods in a month may indicate an underlying issue.
Also Check: Can You Donate Plasma On Your Period
How Is Heavy Menstrual Bleeding Treated
Treatment depends on what’s causing your bleeding, how severe your bleeding is, your health, age and medical history. Also, treatment depends on your response to certain medicines and your preferences. For instance, you may not want to have a period at all, or you may want to reduce your bleeding. In addition, your plans to get pregnant will affect your treatment options.
Talk with your provider about your health concerns and your goals for treatment.
Medications used to treat heavy menstrual bleeding
- Iron supplements improve your iron stores.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs like Ibuprofen® or Aspirin® can ease your cramps and reduce your bleeding.
- Birth control may help make your periods more regular and lighten your blood flow.
- Hormone therapy can help balance the amount of estrogen and progesterone in your body so that your menstrual flow isn’t as heavy. HT is often recommended for heavy menstrual bleeding associated with perimenopause but comes with risks that you should discuss with your provider.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists can temporarily stop or reduce bleeding by preventing ovulation.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists can manage heavy period bleeding related to fibroids.
- Desmopressin nasal spray can stop bleeding associated with von Willebrand disease by helping your blood clot.
- Antifibrinolytic medicines, like tranexamic acid, prevent clots from breaking down and causing excessive bleeding.
Procedures used to treat heavy period bleeding
What Causes Excessive Menstrual Bleeding
Excessive menstrual bleeding can be an indication of many things. While irregular periods are a normal symptom of menopause, it’s best to speak to a doctor to determine whether or not there is an underlying medical condition. The following conditions are some of the most common causes of excessive bleeding.
Recommended Reading: 90 Day Probationary Period Template
Diagnosis Of Painful Periods And Heavy Bleeding
UT Southwesterns experienced gynecologists conduct a thorough evaluation, which includes a:
- Physical exam
- Review of personal medical history, including details of the patients menstrual cycle
- Discussion of symptoms
Patients should bring information about the dates and lengths of their last several periods. For sexually active patients, a pelvic exam will be performed to check for infections and to examine the cervix.
To diagnose heavy bleeding and painful periods, our doctors usually recommend one or more tests, such as:
- Blood tests to look for signs of iron deficiency, thyroid disorders, or blood-clotting abnormalities
- Ultrasound: Diagnostic tools that use sound waves to produce images of the pelvic organs. Used to look for any abnormalities
- Pap smear: Sample of cells from the cervix that are examined under a microscope for infection or changes that can lead to cancer or already are cancerous
- Endometrial biopsy: A test that samples a small amount of endometrial tissue for examination under a microscope
- Magnetic resonance imaging scans: Equipment that uses a large magnet and radio waves to produce detailed images of pelvic organs
Based on the results of these tests, we might recommend further testing, such as:
How Do Bleeding Disorders Affect Pregnancy
Women with bleeding disorders are at risk of complications during and after pregnancy:
- Bleeding during pregnancy
- Dangerous bleeding after childbirth
If you have a bleeding disorder and are thinking of becoming pregnant, talk to your doctor first. You may also want to find a doctor who specializes in high-risk pregnancies.6 Because bleeding disorders run in families, your baby may also have a bleeding disorder.
Read Also: Usaa New Car Insurance Grace Period
Could It Be A Coagulation Problem
Although most people with a coagulation problem are likely to have had menorrhagia at a young age and therefore be diagnosed, it is possible for clotting problems to occur later in life. Bleeding disorders can occur during perimenopause and those that do have sudden heavy bleeding should be investigated.12 Medication such as warfarin, heparin, or steroids can also effect your clotting, as can disorders of the liver, thyroid, bone marrow.
Besides the causes stated above, there are many other causes of heavy periods that occur at a younger age that still apply to those going through menopause, such as pregnancy and infection. If you are having periods, it is possible to become pregnant no matter your age.
Heavy periods are becoming more common due to the rise in body mass index of the general population. Adipose tissue produces oestrogen which has the same effect on your endometrium as the oestrogen from follicles. If heavy bleeding is new to you, you should see your doctor. Endometrium exposed to prolonged periods of oestrogen can result in a condition called endometrial hyperplasia which can be a precursor to cancer. However, the risk of developing endometrial cancer with simple hyperplasia is low less than 5% over 20 years.13
Your heavy periods may be nothing or it could be an indicator that something else may be going on inside your body. We as doctors would be very happy to see you as we want to be able to rule out anything serious.
Is My Heavy Bleeding Just A Normal Part Of Menopause
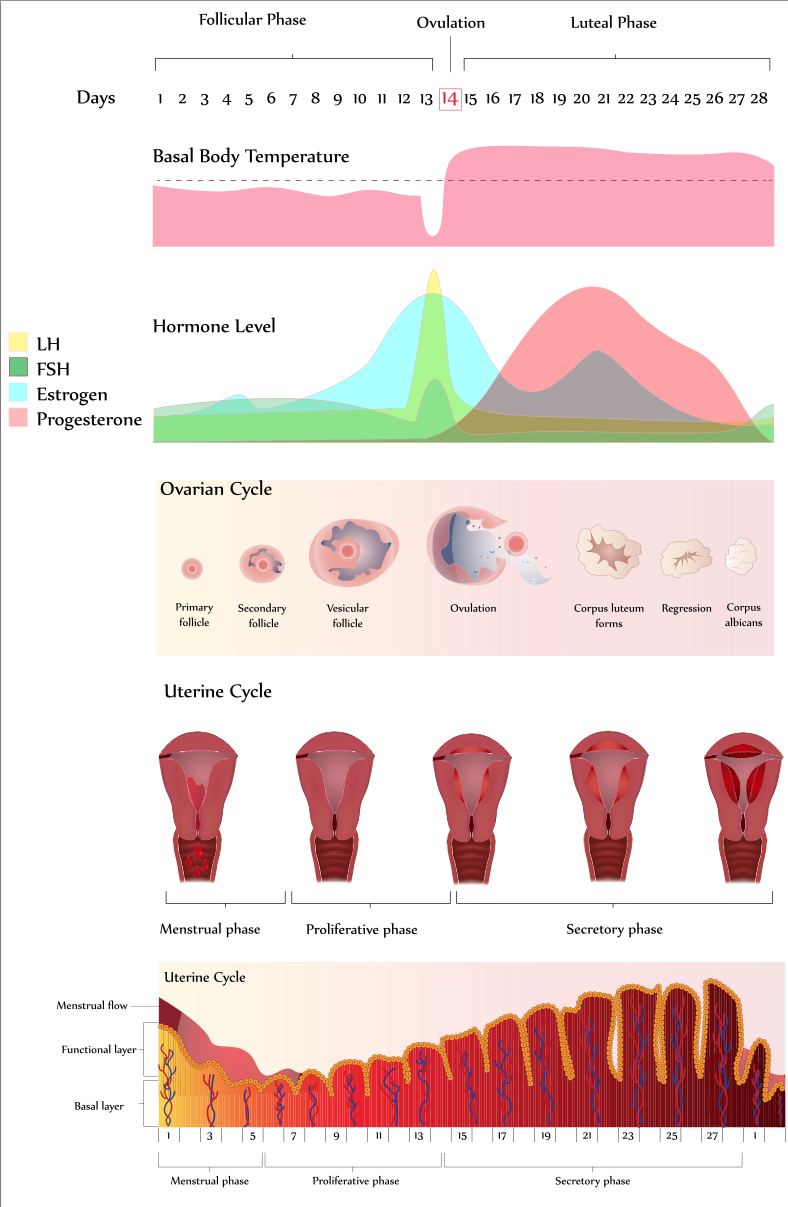
The most common cause of heavy periods during menopause is hormonal imbalance. During the beginning of a normal menstrual cycle, a hormone called follicle stimulating hormone rises which stimulates follicles to mature in the ovaries. Many follicles are stimulated during a cycle and these follicles produce oestrogen which is required to thicken the lining of the womb . Only one follicle will be mature enough to be ovulated.
As there is a decline in the number of follicles at perimenopause, the body tries to recruit as many as possible at the beginning of the cycle. It does this by increasing FSH levels. This part of the cycle can take longer than usual as it becomes harder to recruit eggs. There is an increase in oestrogen from the many follicles stimulated. These higher levels of oestrogen act on the endometrium during the long stimulation period, making it thicker and resulting in heavy periods.2
Ovulation is required for a period to occur. The progesterone produced by the ovulated egg, and its subsequent withdrawal, is what causes a period. During the perimenopause, anovulation becomes more frequent. Thus there is still oestrogen production by the follicles causing the endometrium to thicken, but no progesterone. The endometrium only continues to thicken. Eventually the lining outgrows its blood supply and breaks down, resulting in shedding which is seen as irregular and/or prolonged and/or heavy bleeding.
Also Check: Dark Brown Discharge Instead Of Period
So What Does An Abnormal Period Actually Mean For Your Fast
We are in the thick of Ramadan and guess what else is right around the corner? My period. YAY! I love cramping, feeling fatigued and practically dying from my uterus contracting. Lets not forget the loads of pads I will go through, and the possibilities of an accident happening. Being a girl is so much fun! With that being said, during the month of Ramadan, women who are on their period are not obligated to fast until their period is done. These are the off days for Muslim women who participate in fasting.
Now, it is no secret that when a woman is menstruating, she is not able to partake in fasting. A female will experience a period monthly, sometimes more often than once a month. The true questions lies within our minds as to how many days a women is considered to be done with her period so she is able to fast again.
What Are The Complications Of Menorrhagia
Menorrhagia can lead to various complications. A loss of blood can result in an inherited anemia resulting from menorrhagia. You may also feel cold, exhaustion, fatigue, lack of energy, weakness, and shortness of breath due to anemia. If you need to have a blood test to check for anemia, your doctor can recommend it.
Read Also: 90 Day Probationary Period Letter
What Are The Symptoms Of Menorrhagia
If you have to change your pad or tampon every 1 to 2 hours because it is soaked, or bleed longer than 7 days, see your doctor. Spotting or bleeding between periods is also a sign of a problem.
The symptoms of menorrhagia may look like other conditions or medical problems. Always consult your healthcare provider for a diagnosis.
Cancer Of The Endometrium

Cancer that affects the endometrium of the uterus can cause bleeding in women especially after 40 years. However, younger women may have prolonged heavy period, abdominal pain and vaginal pain during intercourse.
If your doctor suspects cancer as the cause of your long heavy periods, removal of the uterus or hysterectomy will be performed. Removal of the uterus with radio or chemotherapy can achieve cure if done early.
Don’t Miss: Employee Probationary Period Template
What Is Prolonged Period
Women period is due to endometrial shredding that occurs during your menstrual cycle. It occurs due to the interplay of many hormones like estrogen and progesterone.
If your period lasts between two and seven days, then its normal. Women can have periods that last for three days or longer periods that last up to six to seven days. This is normal.
However, any menstrual blood flow more than seven days is considered abnormal.
Period blood flow more than seven days is prolonged and requires urgent treatment. Long periods, in women of reproductive age, can prevent pregnancy or cause infertility.
Whats The Difference Between Bleeding And Spotting During Pregnancy
Spotting is light bleeding. It happens when you have a few drops of blood on your underwear. Spotting is so light that the blood wouldnt cover a panty liner. Bleeding is when the blood flow is heavier, enough that you need a panty liner or pad to keep the blood from soaking your underwear and clothes.
Recommended Reading: 90 Day Employment Probationary Period Template
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Signs of heavy menstrual bleeding include:
- Abdominal pain.
- Periods lasting longer than seven days.
- Passing blood clots that are the size of a quarter or bigger. The blood may appear red, pink, brown, or even rust-like.
- Bleeding through 1 or more tampons or pads each hour for more than two consecutive hours.
- Losing more than 80 milliliters of blood during your period instead of what is typical, 35-40 milliliters.
- Anemia symptoms, like feeling exhausted, tired or short of breath.
With anemia, you may also notice signs of a condition called pica. Pica symptoms include hair loss, pale skin, and the urge to eat non-food items . See your provider if have these symptoms.
How Is Abnormal Uterine Bleeding Diagnosed
Your healthcare provider will ask you several questions when working to diagnose abnormal uterine bleeding. These questions may include:
- What brings on the bleeding?
- What other symptoms are you experiencing?
- Are you pregnant?
Your healthcare provider will then do a physical exam, including:
- A pelvic exam.
- A Pap smear .
Read Also: Usaa Grace Period
What Is The Difference Between Menorrhagia And Menometrorrhagia
Menometrorrhagia was once an umbrella term for two different conditions that sound nearly the same:
- Menorrhagia: excessive and/or prolonged menstruation.
- Metrorrhagia: excessive, prolonged and/or irregular bleeding unrelated to menstruation.
In 2011, the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics changed the names to prevent confusion. Menorrhagia is now called heavy menstrual bleeding. Menometrorrhagia is now called abnormal uterine bleeding.
What Types Of Bleeding Disorders Affect Women
Bleeding disorders in women and girls are often inherited, meaning the disorders run in families. Sometimes bleeding disorders happen when a girl or woman does not have any family history of a bleeding disorder. Women can also develop bleeding disorders as a side effect of certain medicines or from other health problems.
You May Like: Donating Blood While Menstruating
What Is Heavy Menstrual Bleeding
Heavy menstrual bleeding is when your periods are extremely heavy or prolonged. “Heavy” means that your period lasts longer than seven days or that you lose more blood than is typical during menstruation. You may bleed so much that you have to change your tampon or pad every hour for several hours back-to-back. You may pass blood clots the size of a quarter or even larger.
Menstrual bleeding that’s so heavy that it interferes with your daily life is never normal. Your provider can recommend treatments to manage heavy blood flow.
