Antigenic Drift And Shift
Two key processes that influenza viruses evolve through are antigenic drift and antigenic shift. Antigenic drift is when an influenza virus’s antigens change due to the gradual accumulation of mutations in the antigen’s gene. This can occur in response to evolutionary pressure exerted by the host immune response. Antigenic drift is especially common for the HA protein, in which just a few amino acid changes in the head region can constitute antigenic drift. The result is the production of novel strains that can evade pre-existing antibody-mediated immunity. Antigenic drift occurs in all influenza species but is slower in B than A and slowest in C and D. Antigenic drift is a major cause of seasonal influenza, and requires that flu vaccines be updated annually. HA is the main component of inactivated vaccines, so surveillance monitors antigenic drift of this antigen among circulating strains. Antigenic evolution of influenza viruses of humans appears to be faster than influenza viruses in swine and equines. In wild birds, within-subtype antigenic variation appears to be limited but has been observed in poultry.
How Long Should I Stay Home With The Flu
Staying home when you have the flu is important to help you rest and help avoid getting other people sick. The CDC recommends that people with the flu, or people who think they have the flu, should stay home from work at least four to five days after their first symptoms. The CDC also recommends that people with a fever stay home at least 24 hours after their fever goes away without taking any fever-reducing medications. If youre at work and you start to have flu-like symptoms, its best to go home to prevent your coworkers from getting sick.
Preventing The Flu After Exposure
Although there are various products and remedies that may claim to help prevent illness once you’ve been exposed to the flu, none of them have proven to be effective. Your best bet to prevent the flu is to get your annual flu vaccine. Although it’s not 100 percent effective at preventing the flu, it gives you a much better chance of avoiding the illness than anything else.
If you are exposed to someone with the flu, avoid close contact with the person and wash your hands frequently.
- Vitamin C: Although vitamin C is widely used and has many benefits, there is no scientific proof that it will help you avoid an illness such as the flu or a cold.
- Humidifiers: Evidence suggests that viruses such as the cold and flu spread more easily in cold, dry air. This is one of the reasons that they’re more common during the winter. Running a humidifier in your home during the winter can help keep your nasal passages moist. And while there’s no guarantee that this will prevent you from getting sick, it can’t hurt .
- Antiviral medications: If you’re at high risk for complications from the flu and you know you were exposed to it, talk to your healthcare provider about taking antiviral medications. It can help prevent influenza in some people and will reduce the severity of the symptoms in those who do get it.
Don’t Miss: Missed Period On Birth Control Pill
Factors Influencing Clinical Illness
The proportion and duration of illness were lower in the case of elevated pre-HAI titers. In two different studies with A/H3N2 virus challenge, the pooled proportions of illness were 57 percent in participants with pre-HAI titers < 1/12, 52 percent in participants with pre-HAI titers between 1/12 and 1/24, and 15 percent in participants with pre-HAI titers > 1/24 . The mean duration of illness was 4.4 days in participants with pre-HAI titers of 1/8 versus 1.0 day in those with pre-HAI titers of > 1/8 challenged with a wild-type A/H1N1 virus .
What Is Influenza A
Influenza A is a type of virus that causes influenza , a highly contagious respiratory illness. If you get it, you will need to rest at home and avoid infecting others. Vaccination can protect you against influenza A.
Although coronavirus , is a viral illness that has developed into a pandemic, the virus that causes COVID-19 is different from the one that causes influenza.
Both the influenza A and influenza B viruses circulate in the community and change continually, with new strains coming out each winter. This is why yearly vaccination is recommended.
Recommended Reading: Best Time To Conceive A Baby After Periods
What Problems Can Happen
Some children are more likely to have problems when they get the flu, including:
- kids up to age 5, especially babies
- people with a weak immune system from medicines or illnesses or illnesses
- people with chronic medical conditions, such as asthma or diabetes
- kids or teens who take aspirin regularly
- people who are very obese
- women who are pregnant, trying to get pregnant, just had a baby, or are breastfeeding
- people who live in long-term care facilities, such as nursing homes
- people 65 years and older
If they get the flu, their illness can be more serious. They can develop pneumonia or get even sicker from other kinds of infections . If this happens, many will need medical care in the hospital. So it’s important for them not to be near anyone who has the flu or flu-like symptoms.
People who have flu symptoms should keep their distance from anyone who might get very sick if they catch the flu.
Managing Your Symptoms At Home
If you’re otherwise healthy, you can look after yourself at home by resting, keeping warm and drinking plenty of water to avoid dehydration.
If you’re concerned about coronavirus , be mindful of our ibuprofen advice on the coronavius page.
If you feel unwell and have a fever, you can take paracetamol or anti-inflammatory medicines such as ibuprofen to lower your temperature and relieve aches. Children under 16 shouldn’t be given aspirin.
Stay off work or school until you’re feeling better. For most people, this will take about a week. See your GP if your symptoms get worse or last longer than a week.
Read the page on preventing flu for more information about stopping the infection spreading to others.
Recommended Reading: Why Am I On My Period On Birth Control
How Long Does Flu Last And Is It Serious
If you have flu, you generally start to feel ill within a few days of being infected.
You should begin to feel much better within a week or so, although you may feel tired for much longer.
You’ll usually be most infectious from the day your symptoms start and for a further 3 to 7 days. Children and people with weaker immune systems may remain infectious for longer.
Most people will make a full recovery and won’t experience any further problems, but elderly people and people with certain long-term medical conditions are more likely to have a bad case of flu or develop a serious complication, such as a chest infection.
Read more about the complications of flu
Is It Flu Or A Cold
It can sometimes be difficult to tell if you have flu or just a cold, as the symptoms can be quite similar. The main differences are:
Flu symptoms:
- usually include fever and aching muscles
- make you feel too unwell to continue your usual activities
Cold symptoms:
- come on gradually
- mainly affect your nose and throat
- are fairly mild, so you can still get around and are usually well enough to go to work
Don’t Miss: I M 5 Days Late On My Period
What To Expect With Influenza
Symptoms of the flu can hit very quickly and may last several weeks. A bout of the flu typically follows this pattern:
- Days 13: Sudden appearance of fever, headache, muscle pain and weakness, dry cough, sore throat and sometimes a stuffy nose.
- Day 4: Fever and muscle aches decrease. Hoarse, dry or sore throat, cough and possible mild chest discomfort become more noticeable. You may feel tired or flat.
- Day 8: Symptoms decrease. Cough and tiredness may last one to two weeks or more.
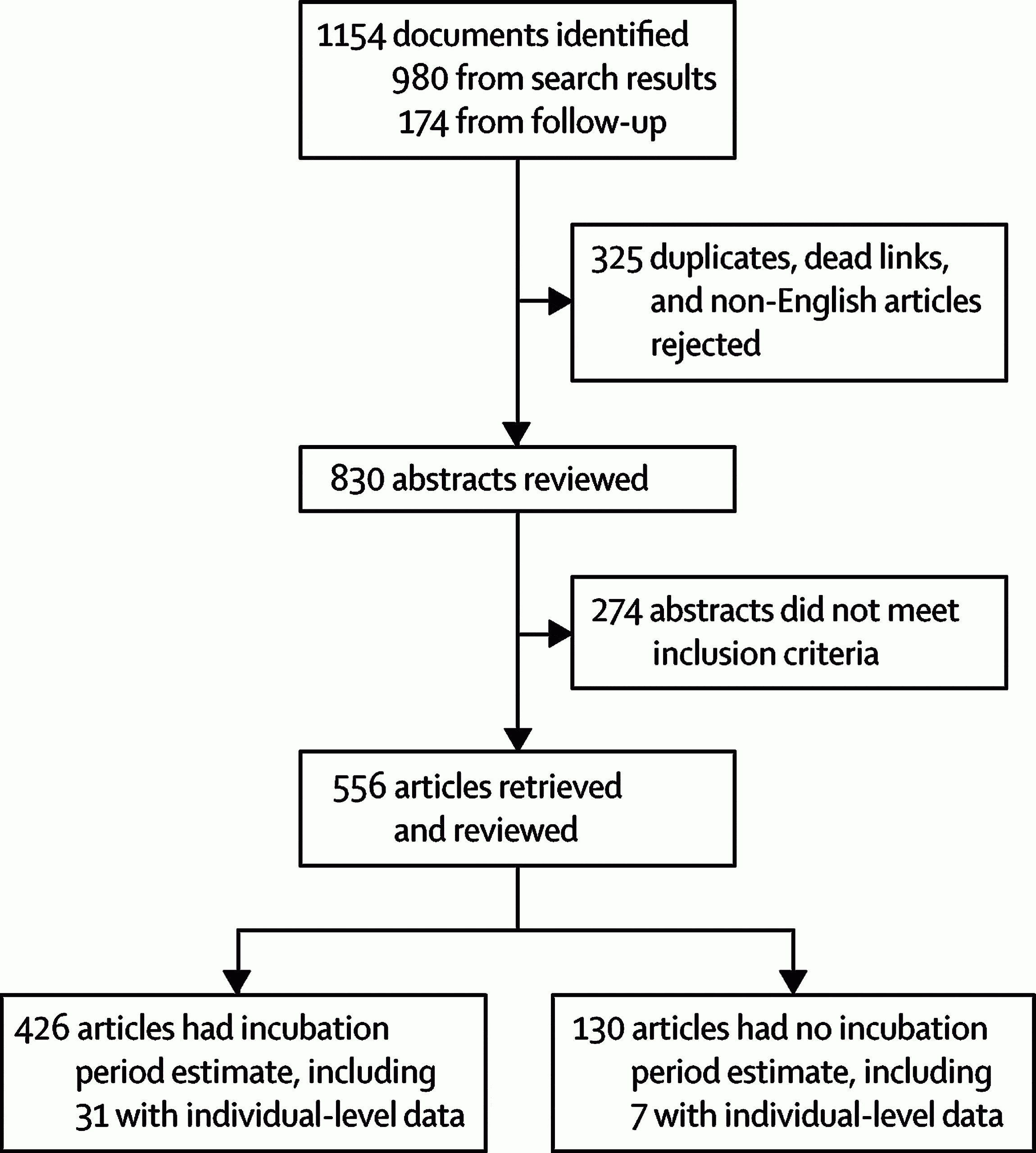
Search Strategy And Identification Of Studies
A literature search was carried out using the PubMed database, with the keywords or influenza, human ) and or experimental or deliberate infection or shedding or symptoms ). We limited our search to English-language papers published between 1965 and 2005. A total of 827 papers were selected . We included any study with any design in which a subgroup of participants was challenged with a wild-type influenza virus and for which there was at least one type of outcome measure, that is, viral shedding or symptoms. We identified additional articles by searching the reference lists of articles. We also made a hand search in textbooks on influenza. We did not specifically consult world-leading specialists on influenza, but a bibliographic search on their names was performed. No attempt was done to retrieve primary data from the original studies. Two of us read all the studies retrieved in the search and applied the inclusion criteria. Differences were resolved by discussion and consensus.
Identification of eligible articles.
Read Also: How To Stop Period For Sex
What Is Influenza
Influenza is a highly contagious viral infection of the respiratory tract that can cause severe illness and life-threatening complications . It affects people of all ages. The flu is usually spread by breathing in droplets from coughs and sneezes that contain the virus.
The flu is a seasonal infection that usually occurs from April to September. Flu seasons vary in severity and duration from year to year. In a year of high influenza activity, it is estimated that the flu can contribute to more than 3,300 deaths in Australia.
Even healthy people can sometimes die from the flu. Some Victorians are at increased risk of serious disease and complications of flu, like young children, the elderly, pregnant women, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people and people with a weakened immune system or a chronic medical condition.
Since the COVID-19 pandemic began, there have been low rates of the flu in Australia due to closed international borders and social distancing measures. However, after borders reopened in 2021, influenza has begun to increase in Australia. Vaccination is key to protecting yourself and those around you from the flu. For more information visit Stay well this winter.
What Is The Flu
Influenza, more commonly known as the flu, is a contagious respiratory infection caused by several flu viruses that infect the nose, throat, and lungs, according to the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases . The flu can be transmitted from person to person through the air via coughing or sneezing or by touching surfaces where there may be live flu viruses, according to Johns Hopkins Medicine.
Each year, the flu makes millions of people sick and causes thousands of hospitalizations and flu-related deaths. Anyone can get the flu and spread it to otherseven healthy people, the NIAID says. The virus can be especially risky for certain groups, including the very young, elderly, pregnant women, and people with certain medical conditions.
People who get infected with the flu may develop symptoms like fever, chills, muscle aches, coughing, congestion, headache, and fatigue for about a week. Of note, since symptoms of the flu can also be the symptoms of other illnesses, you should see your healthcare provider to get confirmation of a flu diagnosis, per Johns Hopkins Medicine.
Most patients with the flu get better within two weeks, but some people can develop serious complications, like pneumonia, the NIAID notes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention also indicate other possible flu-related complications in moderate to severe cases, which include sinus and ear infections inflammation of different organs or muscle tissues and multi-organ failures.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Period
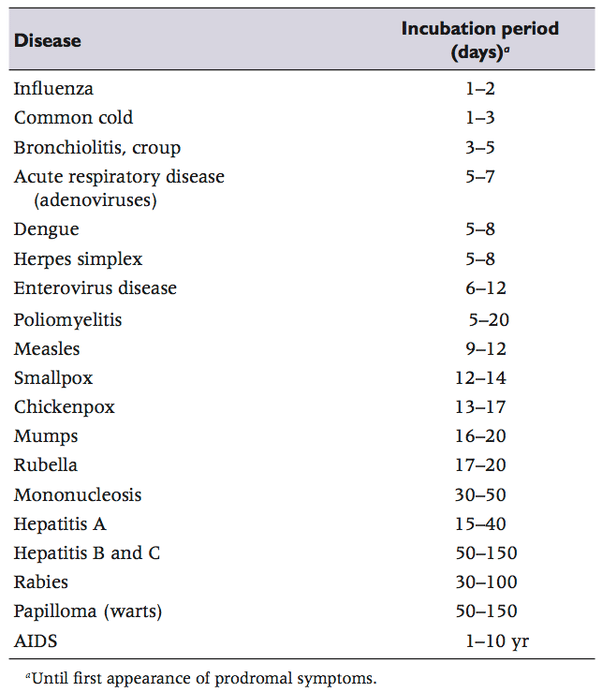
How Long Is The Incubation Period Of The Flu
There’s no exact time frame that’s the same for every person with the flu. In general, the CDC says that the incubation period of the flu can range between one and four days, with the average length of time being two days.
Once people with the flu are showing symptoms, they are most contagious three to four days after illness begins, per the CDC. This time period can coincide with the incubation period. Most healthy adults may be able to infect others starting the day before they show symptoms and continue to be infectious up to seven days after they become sick, the CDC adds.
“People have the flu and are out and about doing their regular stuff, coming into contact with others before they get sick,” Dr. Boling said. “You can infect plenty of people during that time.”
Susceptibility And Resistance To Influenza
When a new influenza strain appears, all people are susceptible, except those who have lived through earlier epidemics or pandemics caused by a related strain.
Infection produces immunity to the specific infecting virus, but the duration and breadth of immunity may vary widely. This is partly dependent on host factors, the degree of antigenic change in the virus and the time since the previous infection.
Also Check: Can You Have Regular Periods And Not Ovulate
How Is The Flu Treated
Most kids with flu get better at home. Make sure your child:
- drinks lots of liquids to prevent dehydration
- gets plenty of sleep and takes it easy
- takes acetaminophen or ibuprofen to relieve fever and aches. Don’t give kids or teens aspirin because of its link to Reye syndrome.
- wears layers that are easy to remove. Kids might feel cold one minute and hot the next.
Children with the flu should stay home from school and childcare until they feel better. They should go back only when they haven’t had a fever for at least 24 hours without using a fever-reducing medicine. Some kids need to stay home longer. Ask the doctor what’s best for your child.
Doctors may prescribe antiviral medicine for a very ill child or kids are at risk for more serious symptoms. The medicine can shorten the flu by 12 days. It works best if children start taking it within 48 hours of the start of the flu. If a doctor prescribes antiviral medicine for your child, ask about any possible side effects. Doctors won’t prescribe antibiotics for the flu. Antibiotics work only against bacteria, not viruses.
Patients With Uncomplicated Seasonal Influenza:
Patients that are not from a high risk group should be managed with symptomatic treatment and are advised, if symptomatic, to stay home in order to minimize the risk of infecting others in the community. Treatment focuses on relievingsymptoms of influenza such as fever. Patients should monitor themselves to detect if their condition deteriorates and seek medical attention Patients that are known to be in a group at high risk for developing severe or complicated illness, should be treated with antivirals in addition to symptomatic treatment as soon as possible.
Patients with severe or progressive clinical illness associated with suspected or confirmed influenza virus infection should be treated withantiviral drug as soon as possible.
- Neuraminidase inhibitors should be prescribed as soon as possible to maximize therapeutic benefits. Administration of the drug should also be considered in patients presenting laterin the course of illness.
- Treatment is recommended for a minimum of 5 days, but can be extended until there is satisfactory clinical improvement.
- Corticosteroids should not be used routinely, unless indicated for other reasons as it has been associated with prolonged viral clearance, immunosuppression leading to bacterial or fungal superinfection.
- All currently circulating influenza viruses are resistant to adamantane antiviral drugs , and these are therefore not recommended for monotherapy.
You May Like: Can Birth Control Stop Your Period Forever
Lineages Of Influenza A Viruses
Avian influenza A viruses that infect birds have evolved into distinct genetic lineages based on the geographic locations where they were first detected. These different lineages can be distinguished by studying the genetic make-up of these viruses. For example, avian influenza A viruses that were first detected in birds in Asia can be recognized as genetically different from avian influenza A viruses that were first detected among birds in North America. These broad lineage classifications can be further narrowed by genetic comparisons that allow researchers to group the most closely related viruses together. The host, time period and geographical location are often used in the lineage name to help further delineate one lineage from another.
Avian influenza A viruses are classified into the following two categories: low pathogenicity avian influenza A viruses, and highly pathogenic avian influenza A viruses. The categories refer to molecular characteristics of a virus and the virus ability to cause disease and mortality in chickens in a laboratory setting pdf iconexternal icon. HPAI and LPAI are defined and explained below:
Avian Influenza A Viruses
Avian Influenza A Viruses
Avian Influenza A Viruses
Avian Influenza A Viruses
Avian Influenza A Viruses
How Can I Tell If Im Still Contagious
It can be hard to tell if youre still contagious even after youve recovered from the flu. Its possible to have the flu for a few days, feel better, and still be contagious days later. In other words, just because you feel better, this doesnt mean you cant pass the virus on to someone else. The best way to know if youre still contagious is to count how many days it has been since the day you got sick. If its been seven days or longer since you first started getting symptoms, you probably arent contagious anymore.
The flu is contagious regardless of whether or not you have a fever. Youll still be contagious for five to seven days even if your fever breaks early on. The time it takes to no longer be contagious is just a matter of where you are on the seven-day timeline.
Don’t Miss: Is Missed Period A Sign Of Pregnancy
