Causes Of Vaginal Bleeding Between Periods
Bleeding between periods isnt a normal part of the menstrual cycle.
The average cycle lasts 21 to 35 days. Normal vaginal bleeding, also known as your period, can happen for a few days to a week. Any bleeding outside of this is considered abnormal and can be caused by a variety of factors. These include:
Spotting Between Periods: Complications
Abnormal vaginal bleeding may be minor. But it could signal something more serious or even life-threatening, such as a benign growth like a polyp or fibroid, a bleeding disorder, an infection, or an injury. Itâs rare, but spotting can sometimes be a sign of cancer. To be safe, have your doctor check it out.
Show Sources
Changes In Hormone Levels
A common cause of spotting before or between periods is changes in hormone levels. Womens cycles are ruled by hormones and any sudden fluctuations in those hormone levels can cause unexpected bleeding or spotting.
Among the reasons for hormonal changesmany of which are entirely benignis the use of hormonal birth control. If you have recently started a new birth control pill or other hormonal birth control it may take a few months for your body to adjust. The changing levels of hormones can cause spotting for a week or a few days. Failing to take your pill at the same time every day may also lead to spotting.
Many women report spotting during ovulation, which is attributable to the changes in estrogen levels at that time of the month. Just before ovulation , levels of estrogen rise. Once the egg is released, estrogen decreases as progesterone increases. It is this shift in balance between the two hormones that can cause ovulation spotting. For some women who are trying to conceive, this can be a useful sign to help them know when ovulation is occurring.
Recommended Reading: Exercises To Make Your Period Come Faster
What Causes Abnormal Bleeding
- Polyps: growths, or small clumps of cells, that form when cells in the lining of the uterus overgrow
- Adenomyosis: the result of tissue that normally lines the uterus growing into the uterine wall
- Leiomyoma: benign tumors in the uterus, often called fibroids
- Malignancy and hyperplasia: when the lining of the uterus becomes too thick
- Coagulopathy: when the bodys ability to clot is worsened, usually due to reduced levels or absence of blood-clotting proteins
- Ovulatory dysfunction: a very common cause of abnormal bleeding and occurs when ovulation is abnormal, irregular, or absent
- Endometrial: abnormal functioning of endometrial tissue
- Iatrogenic: when bleeding could be the result of birth control, other hormonal drugs, or other medications
- Not otherwise classified: when doctors cant discern one specific cause for bleeding issues
Bleeding that interferes with life is not normal, and you dont have to live with it. Help is available, whether youre a teen whos just starting to deal with abnormal bleeding or a woman in perimenopause whos struggled for years.
Preparing For Your Medical Appointment

When you see your doctor, she may need to know:
- How long this has been happening: Is it something youve always experienced or did it start recently?
- How often it happens: Is it monthly or irregular? Is this the first time its happened?
- If theres a pattern to the bleeding: Have you observed the bleeding happens on certain days in your menstrual cycle or seemingly at random?
- How long did the bleeding last: 12 days or more?
- How heavy was the bleeding: Did you use any protection? Was a panty liner insufficient?
- Was there anything unusual about the blood: Color, texture, or odor?
- Did you also experience pain or other symptoms while you were bleeding?
- Did the bleeding coincide with any increased physical exertion ?
- Was there anything you did that seemed to make the spotting worse or better?
Your doctor may also examine you. The tests your doctor might recommend will depend on your age and other factors. If you could be pregnant, they will likely obtain a pregnancy test.
They will most likely order bloodwork to check your blood count and see if youre anemic.
Other tests your doctor may recommend in order to determine a cause of abnormal uterine bleeding may include:
Don’t Miss: How To Stop Cramps In Buttocks During Period
When Should I See My Doctor
Bleeding between periods is common in fact, it happens to most women at some point during their lives. However, it is not considered normal to bleed frequently in one month, or to bleed between your periods for several months. Bleeding after having sex should always be discussed with your doctor. There are many possible causes for bleeding between periods and a lot of them arent serious, but you should speak to your doctor if you bleed between periods as it can occasionally signal something serious.
What Causes Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding
When bleeding is not caused by your menstrual cycle, it is called abnormal or dysfunctional uterine bleeding. This is the most common cause of abnormal vaginal bleeding during a woman’s childbearing years. Up to 10% of women may experience excessive bleeding at one time or another. African American women tend to have more episodes. When the complex hormonal processes of the menstrual cycle are interrupted, resulting in estrogen and progesterone levels that are out of balance, excessive vaginal bleeding may occur. This bleeding is related to irregularities of your menstrual cycle without any disease.
The diagnosis of dysfunctional uterine bleeding is a diagnosis of exclusion, which means that all other causes for the bleeding have been considered and determined not to be the cause of the bleeding. Depending on the female adolescent or woman’s age, there are different reasons for the person to have dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
The most common cause of dysfunctional uterine bleeding in a female adolescent is anovulation. In the first two years of a female adolescent having a menstrual cycle, 85% of the menstrual cycles can occur without the release of an egg. As the female adolescent gets older, the percentage of cycles that are anovulatory decreases, and she is more likely to experience normal periods. By the time the a woman has had a menstrual cycle for six years, fewer than 20% of cycles will occur without an egg being released from one of the ovaries.
You May Like: Why Am I Spotting Between Periods
Risks Of Heavy Bleeding Between Periods And Clotting
Depending on the cause of intermenstrual bleeding and clotting, the risks to your health will be different. However, anemia is one risk that is common to all causes.
Anemia is a condition in which you lack enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to your body’s tissues. It can have many causes, including heavy menstrual bleeding or vaginal bleeding between periods .
Anemia doesnt always have symptoms. But, according to the Mayo Clinic, signs and symptoms of anemia include:
What Causes Vaginal Bleeding
There are many causes of vaginal bleeding other than menstruation. You should always work with a healthcare provider to determine the cause of your bleeding. Some of the more common causes are medical conditions, hormones and pregnancy complications.
Medical conditions
- Cancers of the female reproductive system: These can include cancers of your cervix, endometrium , ovaries or fallopian tubes.
- Bleeding disorders: A problem with normal blood clotting can result from an inherited condition such as hemophilia or von Willebrand Disease, a low red blood cell count , a deficiency of Vitamin K or as a side effect of medications .
- Hypothyroidism: An underactive thyroid gland can interrupt normal menstrual cycles.
- Uterine fibroids: Non-cancerous growths that develop from the muscle tissue of your uterus. Their size, number, growth rate and location within your uterus can vary greatly.
- Adenomyosis: A condition where the lining of your uterus grows through the uterine wall.
- Uterine polyps: An overgrowth of cells on the lining of your uterus. Polyps are usually not cancerous, but some can develop into precancerous polyps.
- Severe cervicitis: Cervicitis is inflammation or infection of your cervix.
- Endometrial hyperplasia: The endometrium becomes too thick, usually due to a hormonal imbalance of estrogen and progesterone. This condition isnt cancerous, but in some cases can lead to cancer of your uterus.
Hormones
Pregnancy complications
Other possible causes
Don’t Miss: Is It Possible To Miss A Period For A Month
What Causes Prepubertal Vaginal Bleeding
There are several different reasons why a pediatric patient may experience vaginal bleeding. Some of the most common causes are listed below:
- Urethral prolapse
In the U.S., the average age of the first period is 12 years old. If your child has vaginal bleeding earlier than that, it is important you notify your health care provider.
Treating Prepubertal Vaginal Bleeding
When Birth Control Causes Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding
Birth control pills, patches, implants, injections and rings that contain hormones can cause abnormal vaginal bleeding as a side effect. This can occur:
- During the first few months when a woman begins using hormone-based birth control.
- When changing the type of birth control pill or the dose of estrogen.
- When a woman does not take her birth control pill correctly, missing doses or not taking them at the same time each day.
- After using birth control for a long time, which can affect the lining of the uterus and cause bleeding.
- During the first few days of using an intrauterine device , one either with or without the synthetic hormone progestin some women continue to experience spotting between periods with an IUD.
- When using the Depo-Provera birth control injection.
- When using a birth control implant.
It is important to check with a health care provider to determine the cause of abnormal vaginal bleeding. It may be due to one of the birth control issues above, which should be monitored.
You May Like: What Age Are You Supposed To Get Your Period
Changes To Your Hormone Levels
Young women often spot, or bleed very slightly, when they ovulate . It happens about 10 to 14 days after their period and is usually caused by a temporary drop in levels of the hormone oestrogen. This is quite normal.
As well as reduced oestrogen levels, you may also experience other hormonal imbalances, which are completely harmless. This could be as a result of stress, or a recent change of diet.
Girls who have just started their periods and women going through menopause are more likely to have irregular periods, which can be confused with bleeding between periods.
Your doctor may organise a blood test to investigate your hormone levels and will advise you on possible treatments.
Changes To The Cervix
Bleeding between your periods may be caused by changes in the cells of your cervix. This may be due to inflammation, hormonal changes, a Human Papilloma Virus infection or cervical cancer. If you have bleeding between your periods, your doctor will be able to examine your cervix using a speculum and can take a sample of cells for a cervical screening test.
Also Check: I M 11 Days Late On My Period
Uterine Or Cervical Polyps
Both uterine and cervical polyps can cause spotting before periods. Cervical polyps are growths on the cervix that are usually benign and produce symptoms such as spotting, increased vaginal discharge, heavier periods, and bleeding after sex. Uterine polyps are similar, but grow in the uterus and are more common in women who are 40-50 years old than in younger women. Symptoms include irregular periods, heavy periods, spotting between periods, spotting after menopause, and infertility.
What Is Normal Menstrual Bleeding
Normal menstrual bleeding lasts for about five to seven days. The average menstrual cycle has about 28 days between periods, but it’s still normal to have a cycle that’s anywhere from 21 to 35 days.
Most people who menstruate get to know their cycles over time. Although it may seem like you are losing a lot of blood, it usually only adds up to around 2 to 3 tablespoons per period.
About 14 days after the start of your period, your ovaries release an egg. This is called ovulation. Some people notice spotting during ovulation, which can be normal. However, you should tell your provider if you notice it.
If the egg is not fertilized, a period starts approximately two weeks after ovulation. During a period, the uterine lining is shed because it’s not needed to support a pregnancy.
Verywell / Jessica Olah
Don’t Miss: How Long Does The Average Period Last
Presence Of Ovarian Cyst
If someone has an ovarian cyst and that ruptures, it could lead to bright red vaginal bleeding. In most cases, this type of a bleeding would be accompanied by severe cramps. It is better to see a doctor for remedy. Avoid using home cures and any type of external application. A thorough medical checkup is essential.
Initial Actions And Primary Survey
As with any patient in the ED, first consider airway, breathing and circulation in the patient with pelvic pain and vaginal bleeding. Circulation may need to be addressed immediately if the bleeding is heavy or if they have symptoms of poor perfusion such as altered mentation, dizziness, or difficulty breathing. If circulation is inadequate to perfuse the patients brain, this may lead to an airway or breathing problem requiring intubation to protect the airway as well as aggressive volume resuscitation. In the hemodynamically unstable patient, placing two large-bore intravenous lines is a priority, followed by resuscitation with crystalloid fluids followed by blood products if there has been enough blood loss.
If the source of bleeding is suspected to be a potential ectopic pregnancy, the patient’s pregnancy status needs to be established as soon as possible. If positive, it is crucial to determine whether the pregnancy is intrauterine or extrauterine, as a ruptured ectopic is a surgical emergency requiring emergency laparoscopy. Identification of pregnancy location can be accomplished with bedside ultrasonography in the unstable patient. If intrauterine pregnancy cannot be identified on bedside ultrasound, OB/GYN should be consulted immediately for potential surgical management. The LMP and gestational age should be determined as they are important components of the patients history to help guide management.
History and Physical Examination
Pelvic exam setup
You May Like: How To Skip Period On Birth Control Pills
How Do Doctors Diagnose Vaginal Bleeding
Your healthcare provider will ask you questions about your symptoms and health history. Theyll perform a physical exam and pelvic exam. You can expect your provider to ask some of the following questions:
- When did the bleeding start?
- When does it occur in relation to your period?
- Do you bleed during sex?
- How many pads are you soaking per day?
- How long does your menstrual period last?
- How long between each menstrual cycle?
- What medications are you taking?
- Have you had any recent procedures or surgeries?
- Is there a chance youre pregnant?
Your provider may order the following tests to help them find the cause of your vaginal bleeding:
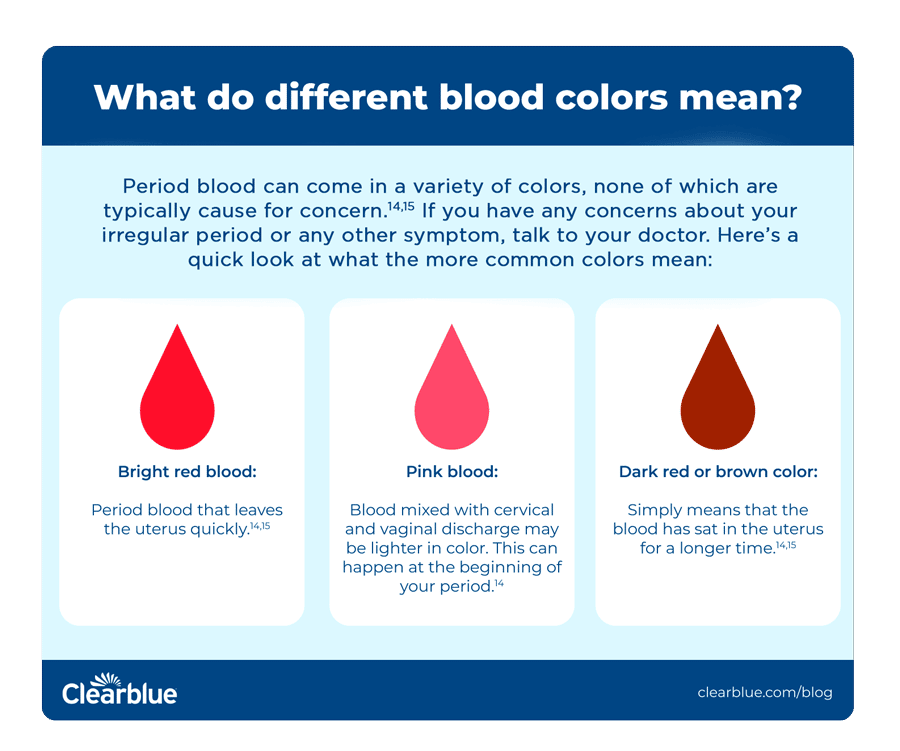
Color Change During A Period
Blood can change in color and texture from month to month or even during a single period.
Hormonal changes, as well as a persons diet, lifestyle, age, and environment, can all cause variations in period blood.
Period blood can vary from bright red to dark brown according to changes in flow. Infections, pregnancy, and, in rare cases, cervical cancer, can cause unusual blood color or irregular bleeding.
People who experience unusually long or heavy periods may require an appointment with a doctor.
Healthy period blood can contain visible pieces of the uterine lining. These small pieces of tissue, or clots, in the blood are not a cause for concern.
However, very heavy bleeding or large clots can be a sign of menorrhagia. According to the , menorrhagia is when a person has unusually heavy menstrual bleeding or periods that last for more than 7 days.
The CDC recommend seeing a doctor if a person has one of the following:
- bleeding that requires a person to change a tampon or pad after less than 2 hours
- blood with clots that are the size of a quarter or bigger
The CDC also list the following as causes of menorrhagia:
- growths on the uterus, such as uterine fibroids or polyps
- hormonal imbalances
Recommended Reading: What Does It Mean When You Have Irregular Periods
Endometrial Resection Or Ablation
Another treatment option is to temporarily remove or cauterize the top layer of the uterine lining . Here the tissue is removed using surgical instruments or destroyed, for instance using laser beams or microwave energy . After this procedure, youll often stop having periods for several years, or have much lighter periods. This option can affect future fertility.
Medically reviewed byDr. Chimsom T. Oleka, M.D, Written by Jane Flanagan Updated on October 9, 2021.
What Do I Do To Prevent Or Avoid Vaginal Bleeding
Some vaginal bleeding is necessary, such as with your menstrual period. However, abnormal vaginal bleeding can be inconvenient and negatively impact your life. Most often, vaginal bleeding is beyond your control and not caused by anything youre doing wrong.
Its best to schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss your symptoms. Talking to them about when your bleeding is happening, what it looks like and how it feels can help them figure out the problem.
You May Like: Does Birth Control Regulate Your Period
What Is Vaginal Bleeding
Vaginal bleeding is any bleeding from your vaginal area. It can refer to bleeding related to menstruation or bleeding unrelated to menstruation such as from trauma or a medical condition. In most cases, vaginal bleeding refers to bleeding thats not related to menstruation .
Bleeding between periods or bleeding outside of a normal menstrual cycle is abnormal vaginal bleeding. This type of bleeding can be random, impossible to predict and may be accompanied by pain or other symptoms. Vaginal bleeding not caused by menstruation can be caused by many factors like:
- Health or medical conditions.
- Injury or trauma.
You may experience spotting or vaginal bleeding at some point in your life. Usually, its not a cause for worry. However, you should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to be sure. In some cases, vaginal bleeding is a sign of a serious condition.
