How Can This Disease Be Prevented
You can take several precautions to avoid contracting this infection. Although it is mild, its better to follow the saying: prevention is better than cure.
- Wash your hands thoroughly: This is important especially after changing diapers and using the washroom. Wash thoroughly with soap and water, and if that is not available, hand wipes or sanitizers will do the trick.
- Clean common areas well: Bedrooms and living rooms are common hub spots of infection. Thats why its important to disinfect these areas with soap and water and then with diluted bleach and water. While youre doing the common areas, clean your childs soft toys, and pacifiers too, since the infection can remain on them for days.
- Teach proper hygiene to your children: Encourage your children to wash their hands before meals, and explain why its best not to put their fingers, or any object in their mouth.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease in children is usually not serious, but it is quite contagious. But, with a couple of home remedies, and advice from your doctor, your child should feel better in a few days. To prevent your child from getting other infections, following a vaccination schedule is important. To help you to keep track of all your childs immunizations, you can also make use of apps like ImmunifyMe. In addition to that, you can schedule appointments with your pediatrician virtually, and even store prescriptions.
How To Stop Hand Foot And Mouth Disease Spreading
Hand, foot and mouth disease is easily passed on to other people. It’s spread in coughs, sneezes, poo and the fluid in the blisters.
You can start spreading it from a few days before you have any symptoms, but you’re most likely to spread it to others in the first 5 days after symptoms start.
To reduce the risk of spreading hand, foot and mouth disease:
- wash your hands often with soap and water and children’s hands too
- use tissues to trap germs when you cough or sneeze
- bin used tissues as quickly as possible
- do not share towels or household items like cups or cutlery
- wash soiled bedding and clothing on a hot wash
Symptoms Of Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Once exposed to HFMD, it can be between three to five days before symptoms emerge. Sometimes, the incubation period can be as long as two weeks. An individual is most contagious during the first week they are ill.
HFMD symptoms include:
- Painful sores inside the mouth
- Skin rash on the hands and feet that may turn into blisters
- It is usually a few days after the onset of the fever that the sores develop in the mouth. The sores which can appear on the tongue, gums or inside the cheeks can be very painful. On the skin, a rash can appear on the palms of the hands or soles of the feet that can turn into blisters. The fever may last only a day or two.
Sometimes a person who has been exposed to HFMD may not have any symptoms or have only mouth sores or just a skin rash.
You May Like: 90 Day Probationary Period Letter
How To Treat Hand Foot And Mouth Disease Yourself
You cannot take antibiotics or medicines to cure hand, foot and mouth disease. It usually gets better on its own in 7 to 10 days.
To help the symptoms:
- drink fluids to prevent dehydration avoid acidic drinks, such as fruit juice
- eat soft foods like yoghurt avoid hot and spicy foods
- take paracetamol or ibuprofen to help ease a sore mouth or throat
How Does A Kid Get Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
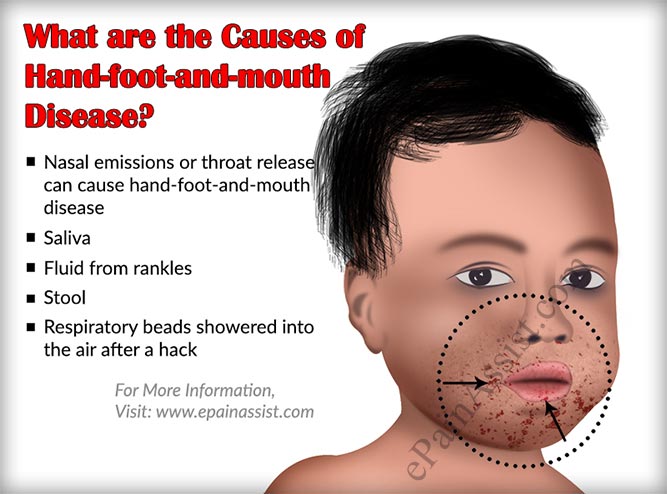
Common areas such as living rooms, or daycare centers are known for immense transmission of germs, and infections. HFMD is spread when a healthy person comes in contact with an infected person that would be a direct transmission. Other ways could be either through indirect contact with saliva or when in contact with infected surfaces.
Also Check: Primosiston To Stop Period
How Is Hand Foot And Mouth Disease Transmitted
HFMD is spread by nose and throat secretions, from the blisters or ulcers, and by feces. In addition, kissing, mucosal contact, and touching objects like toys or other items that have had contact with infected body fluids may spread HFMD. Occasionally, some individuals may get the disease from droplets that are spread in the air. Child care businesses often have outbreaks of this disease. In small wading pools that are inadequately chlorinated, children may transmit the disease to others usually by fecal contamination of the pool water.
For most children and adults, HFMD is a self-limiting disease that resolves with no therapy and does not require treatment by a medical caregiver. However, if symptoms and signs become severe and especially if the individual becomes dehydrated and/or is not acting normally, a medical caregiver should be contacted urgently or the individual should be seen at an emergency department.
Although there is no evidence that HFMD in a pregnant woman affects the fetus, the disease may be transferred to the neonate if the woman has HFMD at delivery. Pregnant women should contact their OB/GYN physician if they suspect they have HFMD during pregnancy.
Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Expert reviewer Dr Adrian Raby, General PractitionerNext review due November 2023
Hand, foot and mouth disease is a common childhood viral illness. It causes blisters on your hands and feet, and ulcers in your mouth. While it may be unpleasant, its generally mild and you usually recover within a week or two.
Hand, foot and mouth disease has no relation to foot and mouth disease, which only affects cattle, sheep and pigs.
Don’t Miss: Usaa Grace Period
Can Adults Get Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
An adult who was never exposed to the viruses that cause HFMD as a child could develop the characteristic symptoms and physical signs if infected by the virus.
- Interestingly, the majority of adults exposed to enteroviruses will remain without symptoms.
- Unfortunately, an infected person is still contagious even though he lacks objective physical findings.
What Are The Complications Of Hand
Complications are uncommon. They include:
- Dehydration due to inadequate fluid intake
- Fingernail and toenail changes are often noted about 2 months after CVA6 infection:
- Transverse lines that slowly move outwards
- Nail shedding about 2 months after the illness.
- Eventually, the nails return to normal.
Serious enteroviral infection can lead to:
- Widespread vesicular rash
Recommended Reading: Employee Probationary Period Template
Tips To Reduce The Spread Of Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
You can do several things to prevent or reduce the spread of hand, foot and mouth disease:
- Wash your hands often, especially after changing diapers.
- Disinfect any contaminated surfaces with a water and bleach or sanitizing wipes.
- Wash your childs clothing, bedding and any other soiled items.
- Stay away from other people, especially during the first few days of the illness. If your child becomes infected, prevent spread by keeping them home from daycare, school or any other group activity. If you are infected, be sure to stay home from work or school.
How Is Hand Foot And Mouth Disease Spread
Hand, foot and mouth disease spreads through direct contact with these blisters, as well as the droplets expelled when you sneeze or cough. The virus can also be passed along in poop, so be sure to wash your hands right away if youre changing diapers, pull-ups or otherwise come in to contact at home or working at a daycare. But its important to note that it can also be passed via shared utensils, towels and clothing, as well as physical contact and by touching contaminated surfaces and toys.
How long is a person with hand, foot and mouth disease contagious?
You are most contagious during the first few days of being sick, often before the blisters appear. Once these blisters dry up, you are less likely to pass on the virus.
Don’t Miss: Can You Donate Blood While Menstruating
Going To School With Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
I donât recommend keeping kids out of school beyond 24 hours after fever â because there are likely several kids in class with it anyway without the fever, who donât even know they have it. Keeping kids out doesnât appreciably change the spread.
But I do recommend keeping kids with Hand Foot and Mouth away from vulnerable adults, if possible:
- Affected kids should not be in the same room as vulnerable adults if they have a fever, plus 24 hours after the fever is gone.
- Affected kids should not share the same food or utensils with vulnerable adults while any sores are still present in the mouth or on the body.
- Vulnerable adults should not change diapers or aid with toileting assistance in affected kids for two months.
- Everyone should implement good hand-washing all the way around, after using the toilet and before eating or drinking or putting hands in the mouth.
If others in the family do get sick, the first symptoms usually occur 3-5 days after getting the virus â and they become contagious about the same time .
Last medical review on:
What Should I Do If My Child Has Hand Foot And Mouth Disease

The first thing you can do is contact your physician. They will give you proper advice on how to handle the situation and if any extra treatment is required to soothe the symptoms. In addition to that, you can try a couple of home remedies such as salt water gargling, having ice creams, and avoiding spicy or salty foods.
You May Like: 90 Day Probationary Period Template
Southern Cross Medical Library
The purpose of the Southern Cross Medical Library is to provide information of a general nature to help you better understand certain medical conditions. Always seek specific medical advice for treatment appropriate to you. This information is not intended to relate specifically to insurance or healthcare services provided by Southern Cross. For more articles go to the Medical Library index page.
What Are The Clinical Features Of Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
The typical incubation period of HFMD is 3-5 days but has been known to range from, 2-7 days.
Symptoms usually include:
- Lesions on the dorsal and palmar surfaces of the hands and feet. The progression is from flat pink patches to small, elongated greyish blisters, and, within a week, these peel off leaving no scars.
- Small vesicles and ulcers in and around the mouth, palate, and pharynx. These are sometimes painful, so the child eats little, frets, and may complain of a sore throat or mouth sores.
- Red macules and papules on the buttocks and sometimes on the arms. Lesions can also occur on the genitalia.
Atypical hand foot and mouth disease results in a more widespread rash. Features may include:
- Red, crusted papules
- Involvement of unusual sites such as the ear
- In children with atopicdermatitis, lesions may select skin affected by eczema .
Flat pink patches on the dorsal and palmar surfaces of the hands and feet are soon followed by small elongated greyish blisters. These resolve by peeling off within a week, without leaving scars.
Usually, there are also a few small oral vesicles and ulcers. These are sometimes painful, so the child eats little and frets. There may be a few on the skin around the mouth. In young children, a red rash may develop on the buttocks and sometimes on the arms.
Atypical hand foot and mouth disease due to Coxsackie A6 results in a more widespread rash, larger blisters and subsequent skin peeling and/or nail shedding.
Recommended Reading: 90 Day Probationary Period Form
Meningococcal Meningitis And Meningitis Septicaemia
Meningitis and septicaemia require immediate medical attention.
The bacteria Neisseria meningitidis is responsible for meningococcal meningitis and meningococcal septicaemia . There are 13 known groups of the bacteria, the most common worldwide are A, B, C, W135 and Y. In the UK, groups B and C are the most common. Meningococcal infection is a rare but serious disease and is fatal in around 1 in 10 people with the illness. About 15% of those that recover have long-term complications.
Ringworm Of The Scalp
Infection with animal ringworm starts as a small red spot which spreads leaving a scaly bald patch. The hair becomes brittle and breaks easily. The picture with human scalp ringworm varies from lightly flaky areas, often indistinguishable from dandruff, to small patches of hair loss on the scalp. There may be affected areas on the face, neck and trunk.
Also Check: 90 Day Probation Period Template
How Long Is Hand Foot And Mouth Disease Contagious
Individuals with HFMD can be contagious during the incubation period before symptoms develop and may remain contagious for days or weeks after the symptoms and signs abate. Even people with mild or no symptoms and signs during infection can be contagious. People are most contagious during the first week after symptoms and signs develop.
Check If It’s Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
The first signs of hand, foot and mouth disease can be:
- a sore throat
- not wanting to eat
After a few days mouth ulcers and a rash will appear.
The symptoms are usually the same in adults and children, but they can be worse in babies and children under 5.
It’s possible to get hand, foot and mouth disease more than once.
Read Also: 90 Day Employment Probationary Period Template
Who Is At Risk For Hand Foot And Mouth Disease
Young children have the highest risk for getting HFMD. Risk increases if they attend daycare or school, as viruses can spread quickly in these facilities.
Children usually build up immunity to the disease after being exposed to the viruses that cause it. This is why the condition rarely affects people over age 10.
However, its still possible for older children and adults to get the infection, especially if they have weakened immune systems.
How Does Hand Foot And Mouth Disease Affect Pregnancy And The Baby

Commonly, HFMD is an illness of children less than 10 years of age adults generally were exposed during childhood and maintain a natural immunity.
- Information regarding fetal exposure to HFMD during pregnancy is limited.
- No solid evidence exists that maternal enterovirus infection is associated with complications such as spontaneous abortion or congenital defects.
- However, should a baby be born to a mother with active HFMD symptoms and signs, the risk of neonatal infection is high.
- While such newborns often have a mild illness, a newborn infant is highly vulnerable and may develop an overwhelming and potentially fatal infection involving vital organs such as the liver, heart, and brain, which could be fatal.
Don’t Miss: Donating Blood While Menstruating
