What Is The Difference Between Pay Period And Pay Date
A pay period is the length of time during which you work, and a pay date is the day on which your team receives their paychecks.
Letâs explore these concepts further.
A pay period is the time frame in which work is being done and paid for. For budgeting purposes, remember this would include any time your team is on the clock, including any onboarding or training time. Pay periods are typically referred to by their number.
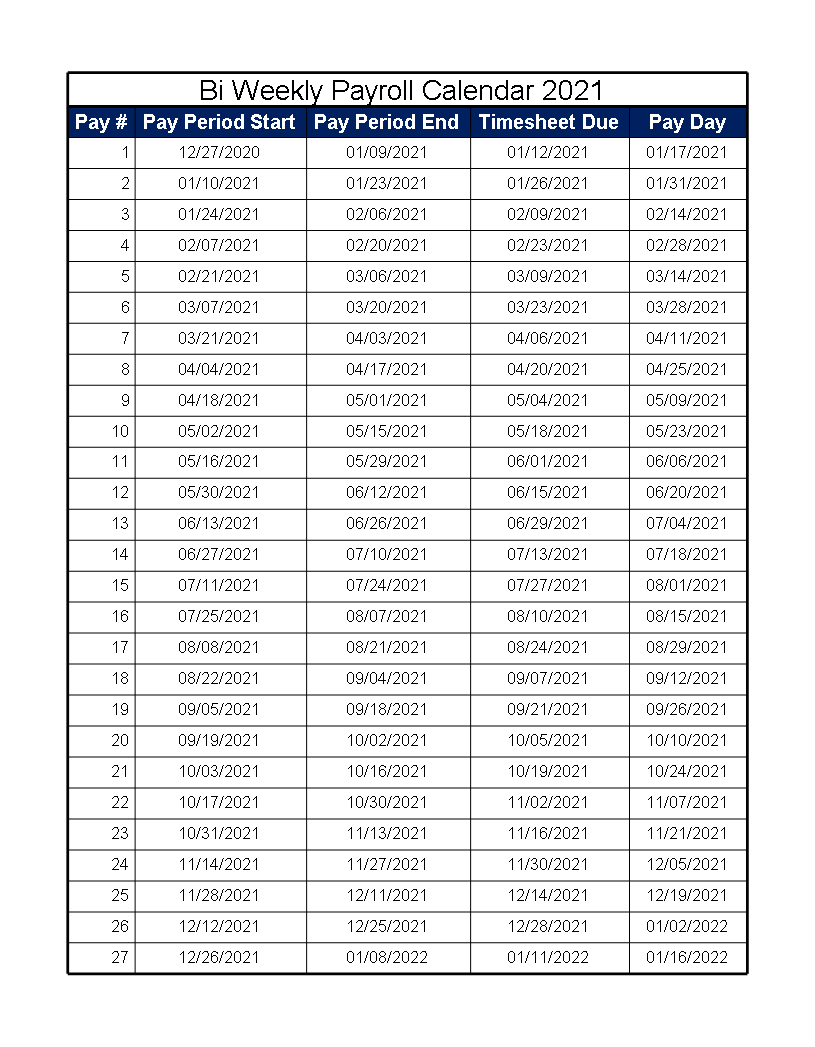
Specifically, a bi-weekly payroll schedule has 26 pay periods per year. So the first two weeks of January would be pay period one, and the second two weeks of January would be period two, and so forth.
A pay date is the date on which companies pay employees for their work. Friday is the most common payday.
It can take a few days to process payroll. Therefore, the last day of the pay period is typically not when employees get paid for their work from that pay period. The pay date for the current pay period might be on the last day of the following pay period. If you use payroll software like Hourly, your employees can see their pay stubs even as payroll is processing.
How Many Pay Periods Are In A Year
There can be as many as 52 pay periods in a year or as few as 12. The number is ultimately determined by the employer unless the workplace or the employees are in a state that has specific payday requirements. Its important for business owners to strike a balance between the cost of running payroll and the financial needs of their staff.
The Best Payroll Software For Your Pay Schedule
As a busy business owner, do you really have the time to manually calculate employee payroll? Maybe you’re still not sure exactly how payroll works and could use a virtual hand.
There are numerous payroll service and software applications on the market today that automate the entire process from beginning to end. Here are just a few choices to consider.
Also Check: 90 Probationary Period Employment Form
How Do You Calculate Biweekly Pay For Salaried Employees
Follow these three steps to calculate biweekly pay for salaried employees:
Tip: Visit our reviews of the best payroll software to learn more about how payroll software can streamline your biweekly pay calculations. You can also learn about one of the best services in our ADP payroll review.
What Payroll Schedule Is Best
No one pays attention when you get payroll right, but it only takes one mistake to break HRs reputation within your organization. And of course, it is crucial you remain fully compliant as well. When you consider these factors, It comes as no surprise that so many HR pros stick with the payroll practices and schedules they inherited from their predecessor.
But your payroll practices should be intentional, not inheritedespecially when it comes to your pay schedule. Many organizations with a mix of exempt and nonexempt employees are already on a monthly or semimonthly pay schedule simply because thats the way it has always been. In HR, thats never a good reason to continue on with difficult measures.
After some consideration, a semi-monthly schedule may seem easier for calculating benefit deductions, however, the division of deductions on a biweekly schedule is not nearly as complicated as it first seems. You can use one of two methods:
divide your employer annual premium by 26 and deduct that from each biweekly paycheck
divide monthly premiums in half and deduct that from each biweekly paycheckexcept for the extra check for those two months with three pay dates.
Though weekly works similarly, having to run payroll half as often still places bi-weekly at an overall advantage.
Employees also tend to enjoy the few months that offer 3 paychecks, which is exclusively associated with biweekly payment methods.
Read Also: Brown Stuff Instead Of Period
Semimonthly Pay Period Length
A semimonthly pay period lasts half of a calendar month. The number of days in a semimonthly pay period depends on how many days there are in the month in question, which is why a semimonthly pay period may involve a different number of calendar days than a bi-weekly pay period.
Employees are only paid twice each month on a semimonthly payroll schedule.
Example of a semimonthly pay period: June 1 – June 15, or February 1 – February 14
What Is The Difference Between Semimonthly Pay And Biweekly Pay
If you are a salaried employee, whether you are paid semimonthly or biweekly does not affect your annual pay. You will receive the same amount every year regardless of the pay schedule. What differs is the amount in each paycheck and how often you receive that check.
For example, if you are earning $50,000 per year and are on a semimonthly pay schedule, each paycheck will be $2,083.33 gross . You arrive at that amount by dividing 50,000 by 24, since there are two pay cycles each month.
On a biweekly pay schedule, your $50,000 annual pay is divided between 26 pay cycles. Therefore, each paycheck will be $1,923.08 every other week before deductions. It may look as if you are paid less, but you receive two additional paychecks each year.
These same figures apply to those who are full-time non-salaried employees. The main difference is each paycheck will be adjusted to account for overtime hours or time off taken within the pay cycle.
Also Check: Dark Brown Discharge Instead Of Period
Can A Business Change Pay Periods
While changing your companys pay period is possible, it shouldnt be done without some considerations. Along with any overtime considerations , ask yourself these questions:
Does your company offer direct deposit? If so, youll need to coordinate with all of the various financial institutions and make sure deposits arent interrupted during the transition. Typically, direct deposit funds are transferred one to two days prior to the direct deposit date.
Do you have payday traditions? If you give employees extra time over their lunch hour to deposit paychecks, provide special office hours for workers in the field to collect their checks or have the CEO hand out checks, consider how changing your pay period will affect these traditions. SHRM advises these traditions may be cherished by employees and changing them may cause negative reactions.
How well do you communicate with your employees? Changing the pay period is a big deal. Your employees count on their paychecks being available on payday. If your communication isnt great, not only will there be confusion but there are also likely to be negative employee reactions. Aside from sending emails and placing notices on bulletin boards, SHRM advises making communication more proactive by hosting a new payday fair. Invite your payroll processor or other vendors to participate. Use the opportunity to educate employees about direct deposit, 401 and other financial planning options.
How Is A Pay Period Calculated
Companies decide what pay period length they want to run their payroll on.
This can be based on a variety of factors, like when the company gets paid for its products and services, how often employees need money, and whether you have hourly employees or if your team is on an annual salary schedule. Thereâs also state law to factor in â you may prefer to pay monthly while state law requires bi-weekly payments.
For example, a company that employs mostly hourly workers might find it beneficial to have a week-long pay period. Weekly payments are easier for financial planning and make employees happier by giving them access to more readily available cash flows.
However, a company that bills its clients at the end of the month and has mostly salaried employees may prefer to pay its employees less frequently â a bi-weekly basis is typical.
You May Like: 90 Day Probationary Period Template
How Can I Keep Track Of My Employees Pay Periods
A popular choice, especially if your business is too small for an in-house payroll manager, is to enlist the help of a payroll service. These payroll services help employers like you track employee hours, set up automated payments and other payroll activities, all in accordance with employee rights. Some payroll services even have HR and accounting specialists to handle employee onboarding, taxes, benefits, paid time off and other factors that affect payroll.
What Is Biweekly Pay
Biweekly pay means you pay your employees once every two weeks, on a set day you choose.
For instance, let’s say you choose to pay your employees once every two weeks, on Friday.
Take a look at the following calendar for the months of January and February, 2019:
Calendar courtesy of Towncalendars.com
As you can see, it doesn’t matter which day of the month you pay your employees — you can pay them on the 4th one month, and then the 1st another. It’s only important you pay once every two weeks.
Once you start the year, you’ll pay your employees once every two weeks. This might sound simple, but that means for two months out of the year, you’ll have three pay periods instead of two.
Don’t Miss: 90 Day Probationary Period Form
Calculating Payroll Dates For Biweekly Salaries Typical Us Payroll Calendar Dates
Calculating US Payroll dates is slightly complicated. First we have to find the first Monday of the year. This begins the first pay-period of 26 pay-periods in America. Then, each payday is exactly 12 days after the starting Monday.
Here is how we can find the first Monday of any given year: =if=2,”1/1/2008″,”1/1/2008″+9-weekday), we are using weekday function to find the day of week on 1/1/2008 and then add required number of days to it to get the First Monday of the year.
Once the first Monday is calculated, then finding the payday dates for each pay period is simple. First payment date is 12 days away from the Monday and subsequent pay dates are 14 days apart.
How To Change Pay Periods
How often you pay your employees can be just as important as how much. Pay frequency is a sensitive issue for both employees and management. All companies need to find a pay frequency that works for them, which minimizes expense and abides by state law. Employees will rely on the payroll schedule you choose and build their monthly budget around it, so striking the right balance is key.
Changing your pay periods is not a decision to be taken lightly. If youre sure its necessary, the least you can do is be fully informed about all the implications.
Don’t Miss: Usaa Grace Period Auto Insurance New Car
How To Calculate Monthly Wages If You Are Paid Every Two Weeks
When you receive pay every two weeks, you may think that it’s the equivalent of being paid twice per month. While usually you do get paid twice per month when you receive bi-weekly pay, sometimes you get paid more than twice in a month, depending on how many weeks are in the month. Because there are 52 weeks in a year, there are 26 bi-weekly pay periods. This means that receiving pay every two weeks will result in a different calculation of monthly wages than if you receive your pay twice per month, so multiplying your check by two will not bring you the correct amount.
Tips
-
If you receive bi-weekly pay, you can calculate your monthly earnings using a simple formula. After multiplying your current wages , you can then divide this sum total in order to calculate your monthly wages.
What Payroll Cycle Is Best For Your Business
When setting up payroll for the first time, take a bit of time to determine which payroll cycle will work best for your business.
Remember that a biweekly pay period is a good choice for those with hourly employees to pay, but if the majority of your employees are salaried, you may be better off choosing semimonthly. Just keep in mind that changing your payroll cycle can negatively affect your employees, so choose wisely.
Read Also: Can You Donate Plasma On Your Period
Hourly Vs Salaried Employees
One of the biggest things to consider when making the decision whether to pay employees biweekly versus semimonthly is the number of hourly employees you currently need to pay.
Its much easier to pay hourly employees biweekly, which runs on a 40 hour work week than it is to pay them semimonthly, particularly if your employees frequently work overtime.
If the majority of your employees are paid hourly, it might be best to opt for biweekly. If theyre salaried, semimonthly may be the way to go.
Types Of Pay Periods & How To Choose
A year can be divided into 52 weeks, 365 days, or 12 months, which means there are numerous schedules you can use for your payroll. Some businesses are more concerned with weekly payouts and opt to pay once a week or every other week. Others divide each month in half and choose to pay in the middle and at the end. Additionally, although not as frequent, a monthly pay schedule works better for some companies. Here are some factors you should consider when determining your pay schedule.
- Average wages: Restaurant employees who earn tipped minimum wage may be better suited for weekly paychecks. Forcing employees who receive low wages to wait two to three weeks for payday could damage morale.
- Company cash flow: Paying weekly means you must have enough cash available to pay more often. Some businesses have cash flow cycles that require more time before bank accounts are replenishedlike stores that sell merchandise on credit.
- Profitability: Processing payroll more often usually costs more money , and some businesses, especially startups, have to manage their expenses more carefully. Using providers like Gusto allows employers to run unlimited monthly payrolls at no extra cost.
Here are some of the most common pay schedules from which you can choose. Keep in mind that certain industries have norms, and you may need to follow your industrys tradition to remain a competitive employer.
You May Like: New Hire 90 Day-probationary Period Template
Determine Total Annual Work Hours Available
You then have to determine how many weeks per year your business operates so that you can calculate how many work hours per year employees are eligible to accrue PTO annually. This hours per year number is used as the denominator when calculating your PTO accrual rate.
The standard available work hours per year used by human resources experts is 2,080. Thats equivalent to the number of weeks per year multiplied by the number of hours the average employee works each year.
Example: ABC Company has a standard 40-hour workweek and is open 52 weeks a year.
Heres the math: 40 hours x 52 weeks= 2,080 hours per year
If you grant your employees two weeks of vacation and PTO each year, that would equal 80 hours per year. Thats your numerator.
Heres the math: 80 hours PTO / 2,080 hours per year= 0.038 hourly PTO accrual rate
What that means is that for every hour worked, the employee in this example would accrue 0.038 hours of PTO. If they worked on average 40 hours a week, or eight hours a day, the accrual rate would be:
| Hourly Accrual Rate | |
| 0.304 hours of PTO for each day worked | |
| Weekly Accrual Rate | 1.52 hours of PTO for each week worked |
To calculate each employees PTO accrual rate correctly, you need to provide data for these three variables described in the steps above. Your results may differ depending on rounding and how many decimal places are used in your calculation. However, our calculator above only rounds up the result, not the interim calculations.
