How Is Hiv Spread From Person To Person
HIV can only be spread through specific activities. In the United States, the most common ways are:
- Having vaginal or anal sex with someone who has HIV without using a condom or taking medicines to prevent or treat HIV. Anal sex is riskier than vaginal sex.
- Sharing injection drug equipment , such as needles, with someone who has HIV.
Less common ways are:
- From mother to child during pregnancy, birth, or breastfeeding. However, the use of HIV medicines and other strategies have helped lower the risk of mother-to-child transmission of HIV to 1% or less in the United States.
- Getting stuck with an HIV-contaminated needle or other sharp object. This is a risk mainly for health care workers. The risk is very low.
HIV is spread only in extremely rare cases by:
- Having oral sex. But in general, the chance that an HIV-negative person will get HIV from oral sex with an HIV-positive partner is extremely low.
Tips For Having Sex During Your Period
More rumors and myths surround the issue of sex than probably any other topic in the universe. This is why it’s smart to listen to science and facts.
For starters, you may be glad to know that no scientific evidence exists showing that having sex during your period is harmful to your health.
Some women even find that having intercourse while menstruating brings several benefits. Among other things, it may be more pleasurable than it is at other times of the month.
It’s important to remember, though, that it is possible to get pregnant during your period. Likewise, concerns about sexually transmitted infections don’t “go away” while you’re menstruating. You should take the same safe-sex precautions as always.
This article explains the benefits of “period sex,” some of the safety considerations you should keep in mind if you have sex during menstruation, and how to plan ahead to reduce some of the messiness you may encounter.
How Could You Get Hiv From Contact With Blood
The risk of HIV transmission through blood comes when the person has a detectable viral load and their blood enters another persons body or comes into contact with a mucous membrane. These are parts of the body with wet, absorbent skin such as the:
- eyes
- inside of the anus
- mouth.
Theres also a risk if blood from a person who has a detectable viral load comes into contact with a cut or broken skin, giving HIV a way through the skin and into someones bloodstream. If blood gets onto skin that isnt broken, there is no risk.
In a medical setting, its possible for HIV to be transmitted by someone accidentally cutting themselves with a blade or needle they have used to treat a person living with HIV.
This is called a needlestick injury. The risk of being infected in this way is very low. However, if someone thinks they have been exposed to HIV through a needlestick injury, post-exposure prophylaxis may be an option.
Recommended Reading: Period Blood Stains On Sheets
How Long Does Hiv Live Outside The Body
Overview
There are many myths and misconceptions about how long HIV lives and is infectious in the air or on a surface outside the body.
Unless the virus is kept under specific conditions, the true answer is not very long.
Although it causes a serious disease that cant be cleared by the body, HIV is very fragile in the outside environment. It quickly gets damaged and becomes inactive, or dies. Once inactive, HIV cant become active again, so its the same as if its dead.
Interpreting The Numberswhat Additional Information Needs To Be Provided
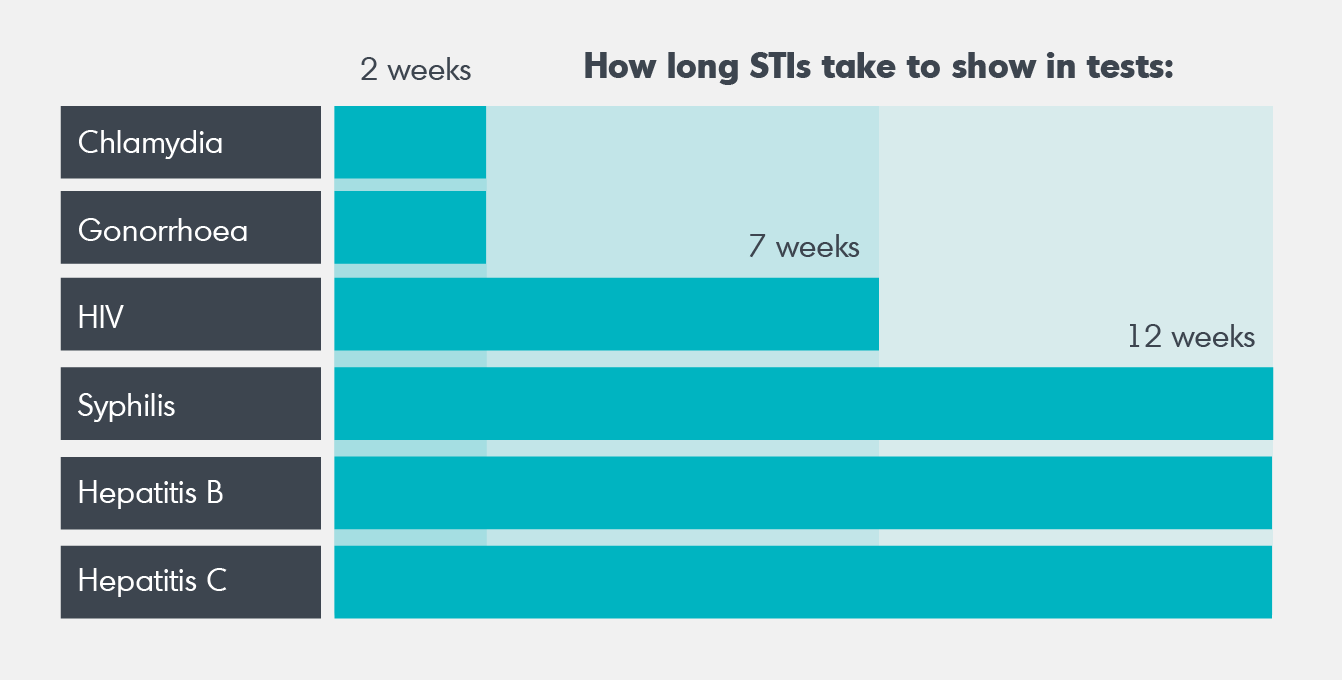
Some clients may see these numbers and think their risk of HIV transmission is low. Therefore, caution is needed when interpreting them. If these numbers are provided to clients, they should be accompanied by information that helps shed light on why the risk may be higher than it seems.
Transmission can occur after one exposure.
It is important to emphasize that a person could become infected from having unprotected sex once or a person could have unprotected sex many times and not become infected, regardless of how low or high the risk per exposure is.
A risk of 1% would mean that an average of one infection would occur if 100 HIV-negative people were exposed to HIV through a certain type of sex. It does not mean that a person needs to be exposed 100 times for HIV infection to occur.
These are estimates of average risk in the absence of biological factors that increase risk.
The numbers in the table above are rough estimates. They are averages and do not represent the risk from all exposures to HIV through a certain type of sex.
The risk of HIV transmission may be much higher than these averages if biological risk factors are present. For example, research shows that STIs and some vaginal conditions, such as bacterial vaginosis, can increase the risk of HIV transmission by up to 8 times.6,7,8 As a result, the risk of an HIV-negative woman becoming infected through unprotected receptive vaginal sex could be closer to 1% if she has a vaginal STI.
You May Like: Employee Probationary Period Template
Myths About Period Sex
Having sex during your partners menstrual period may not be your cup of tea, but then if youve never tried it, how would you know? There are countless religious and cultural taboos that forbid intercourse during that time of the month and youll have to make up your own mind about exactly how you feel about those. But there are also some pretty silly misconception and myths about period sex, especially among guys, that need to be cleared up.
1. Its gross
Look, theres no doubt that period sex has the potential of being a fair bit more messy than sex during the rest of the month, but with a little planning its not gross at all. A towel or an extra sheet spread on your bed will do a discreet mop-up job if necessary. Alternatively, why not do the deed in the shower or the bath tub. Theres nothing like a change of scenery to keep things interesting and any messiness is easily washed away at the turn of a tab.
As another option, you partner may want to try wearing a diaphragm, or a menstrual cap shaped like one, or even a female condom all of which will capture any blood while allowing penetration. If you use a dental dam even oral sex during her period doesnt have to freak you out some guys actually develop a particular, erm… taste for it.
2. Its unhealthy
3. You cant get AIDS or STDs
4. It wont be fun
5. She cant fall pregnant
6. Itll make her period worse
R75 per month
Hiv Medicine And Women
Some medicines can interact with HIV drugs. These interactions can hurt you or make the HIV medicines weaker. You should tell your doctor if you are:
- Using any other prescribed medicines
- Using any recreational drugs, alcohol, herbal remedies, or over-the-counter medicines
- Using hormonal birth control, including the shot, pills, or implant. Some HIV medicines may affect how much of the hormone stays in your system, raising your risk for pregnancy. Talk to your doctor about the type of birth control you use and whether you need to switch to another method.
- Pregnant or planning to become pregnant. This will affect what treatment is best to keep you healthy and prevent HIV transmission to your baby.
HIV medicines also may cause different side effects in women than men.4
- Studies linked the use of nevirapine to a higher risk of rashes and problems with the liver for women with higher CD4 counts.
- Ritonavir may cause more nausea and vomiting in women but less diarrhea in women than in men. Ritonavir is sometimes prescribed to help other HIV medicines work better.
- Other studies show that women are more likely to get fat buildup throughout the body and have problems with the pancreas than men.
Do not change the dose of your medicine on your own. If you are having problems with side effects, talk to your doctor.
Read more about HIV/AIDS drugs and side effects for women at the Food and Drug Administration website.
You May Like: How To Clean Period Blood Out Of Sheets
Questioning The Three Out Of A Thousand Estimate
In a popularly referenced 1989 study, researchers suggested that the risk of acquiring HIV from a single needlestick injury involving HIV-contaminated blood was around 0.32 percent, or roughly three cases out of every 1,000 injuries.
That figure has remained largely stuck in the consciousness of public health authorities, despite growing evidence that the “three out of a thousand” estimate pertained more to untreated source patients with late-stage, symptomatic diseasethe more likely scenario in 1989than to estimates based purely on needlestick injury alone.
A meta-analysis conducted in 2006 largely confirmed those doubts. In reviewing 21 different studies, the researchers found that the pooled estimates suggested that the risk of acquiring HIV was more along the lines of 0.13 percent if the needlestick injury were the only risk factor. Only when the source patient has an AIDS diagnosisnamely, a CD4 count below 200 cells/mL and/or an AIDS-defining illnessdid the estimate rise to 0.37 percent.
What was, perhaps, more important to note was that, of the 21 studies reviewed, 13 concluded an actual risk of 0%. Such disparities in research only served to add to the contentiousness already surrounding the issue of HIV risk in occupational healthcare settings.
If I Am Pregnant And Have Hiv Will My Baby Also Have Hiv
Most women with HIV can protect their baby from becoming infected during pregnancy. Proper pre-natal treatment can reduce the risk that an HIV-positive mother will pass the virus to her child to less than 1 percent. The only way these special treatments can be provided is if the health care professionals know the mother is living with HIV. Treatment is most effective when started early in pregnancy. HIV-positive moms should not breastfeed their babies because HIV is sometimes passed this way.
Recommended Reading: Usaa New Car Insurance Grace Period
To Prevent Hiv Infection Couples Try Testing Together
“There were cases where it was suspected, but not all the pieces were there to say it so clearly as this one,” says Patrick Sullivan, an epidemiologist at Emory University who wasn’t involved in the study.
The circumstances in this case were unique, a spokeswoman for the CDC tells Shots. The couple frequently had sexual contact without a barrier and exchanged blood through rough sex with toys.
The case is a good reminder that HIV can spread during all types of sexual interactions, Sullivan says.
“Anytime there’s intimate contact even through the use of sex toys prevention measures should be taken, especially when there’s a chance of blood contact,” he says.
Hiv Can Spread Through Sexual Contact Between Women
Lesbian couples have a lower risk of spreading HIV to each other than do heterosexual or gay couples.hide caption
toggle caption
Lesbian couples have a lower risk of spreading HIV to each other than do heterosexual or gay couples.
A woman in Texas likely infected her female partner with HIV through sexual contact, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported Thursday.
The case offers the strongest evidence to date that HIV transmission between women, although rare, is possible.
Recommended Reading: 90 Day Probationary Period Policy Examples
Can Hiv Be Transmitted Via Contact With Menstrual Blood
Menstrual blood touching intact skin poses no HIV transmission risk. If it comes into contact with broken skin or is swallowed, then HIV transmission is possible but still unlikely. Due to the effectiveness of HIV treatment, the menstrual blood of someone living with HIV who is adherent to their antiretroviral medication could well have no detectable virus . The small number of case reports documenting HIV transmission via exposure to blood involved a significant amount of blood from the HIV-positive person, as well as open wounds in the other persons skin.
Symptoms Of Hiv/aids And Stages
Many people donât have symptoms at first, and sometimes even for years or decades. But there are signs that can happen, such as flu-like symptoms soon after you become infected with HIV. Even if you donât feel sick, HIV damages the immune system. It hijacks infection-fighting white blood cells called CD4 cells and uses them to churn out thousands of copies of itself. Without treatment, HIV destroys so many of these cells that your body canât protect you from life-threatening infections. If your CD4 count drops below 200, you have AIDS.
There are three stages of HIV infection:
Stage 1: This the earliest stage. You may also hear it called the âacuteâ stage. You might have a fever, rash, fatigue, chills, and other flu-like symptoms. But you might not have any symptoms. If you do, they may start 2-4 weeks after youâre infected. During this time, the virus quickly makes many copies of itself.
Stage 2: During this stage, HIV continues to reproduce, and it slowly damages your immune system over time. You might not feel sick or have symptoms. But HIV isnât gone, and you can still spread it to other people. This stage can last for years or even decades.
Stage 3: This is when you have AIDS. Your immune system has been severely damaged, leaving you vulnerable to other illnesses. With AIDS, many people have symptoms such as chills, fever, sweats, swollen lymph glands, weakness, and weight loss.
You May Like: New Hire 90 Day-probationary Period Template
Other Health Problems That Affect Periods
- A missed period might mean that you are pregnant or that you are starting to go through the menopause.
- Abnormal bleeding or very heavy periods could be signs of a health problem and should always be reported to your doctor.
- Heavy periods can be caused by several factors, including fibroids . If left untreated, the blood loss from heavy periods could lead to anaemia .
How Is Hiv Transmitted
HIV is transmitted between humans through the exchange of certain types of bodily fluids. Bodily fluids that can transmit HIV include blood, semen, breast milk, and vaginal fluids .
Not all body fluids can transmit HIV. The following cannot transmit HIV:
- Exchanging saliva, like through closed-mouth kissing or sharing drinks/utensils
- Coming in contact with an HIV positive personâs tears, sneezes, or sweat
- Ordinary physical contact, such as hugging, hand shaking, or touching shared objects like cutlery, cups, or toilet seats .
- Air or water
- Pets and insects cannot carry the virus and infect you, because transmission of HIV is only between humans .
While care needs to be taken in some situationsâlike when having sex or when open injuries are presentâthis certainly does not mean that it is unsafe to be around people with HIV. Think of how you interact with the vast majority of peopleâbodily fluids are not exchanged. Harboring discriminatory thoughts only perpetuates a fearful stigma against someone with HIV, which only hurts the person who has it.
HIV is often transmitted through sexual activity and drug use in adults in the United States . Maternal transmissionâfrom mother to childâis how the infection is spread to infants .
You May Like: Usaa Grace Period Auto Insurance New Car
